Patch management is a term everyone is familiar with within the depths and limits of endpoint security. While the addition of “automation” to this term may make it seem like one of thousands of other automated tasks, cybersecurity experts have been raving about it over the past few years.
If you are reading this, there is probably no point in explaining to you what patch management automation or automated patch management is. What is actually important for you to understand is how patch management automation affects your business and whether it is really worth it.
We've come a long way from where we started....
Patch management today is an essential requirement to combat vulnerabilities in software, malware or ransomware. A few decades ago, however, patch management was considered a task for the IT administrator and not for the cybersecurity administrator.
Things changed in 2001, with the discovery of a computer worm called Code Red. This was the first mixed attack targeting corporate networks. Within a week, 359,000 hosts were infected, and the virus quickly spread around the world.
This was the beginning. From then on, Microsoft began releasing patches to close all the vulnerabilities and loopholes in the software.
Fast forward to the next decade, the cybersecurity domain witnessed an explosion in the prevalence of threat groups, software vulnerabilities, zero-day exploits and ransomware. From the RSA breach in 2011 to WannaCry and NotPetya in 2017 and finally Follina last year, enterprise network security has always been just a patch away.
Moreover, with more than 100,000 vulnerabilities discovered within the aforementioned time frame, patch management quickly became a fundamental step in securing enterprise networks against vulnerabilities.
2015: Automation
As an enterprise grows, so does its cyber footprint. Unfortunately, the increase in vulnerabilities seems to have outpaced the company’s growth rate. With thousands of vulnerabilities and hundreds of machines to be patched, it was time to eliminate manual efforts.
On March 28, 2012, a patent was filed by International Business Machines Corp on end-to-end patch automation and integration. The abstract of the patent states:
“A method of automating patching a computer system includes determining whether a computer patch is available for a customer computer system, determining a customer patch management policy, determining a customer patch window based on the determined patch management policy, and directing application of the computer patch to the computer system on the determined patch window.”
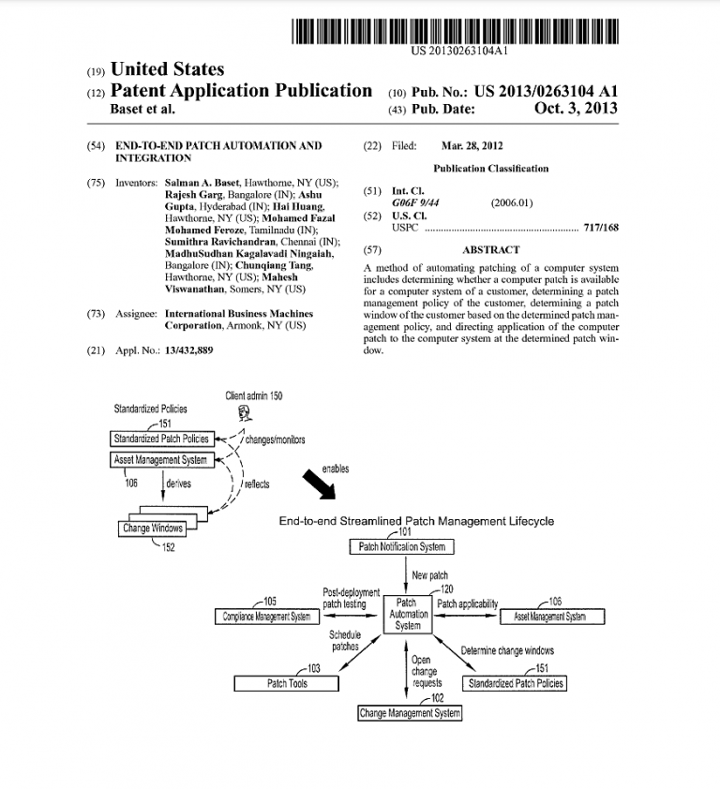
After a few years of successive updates and research, the patent was finally published on March 3, 2015, and has been active ever since. In the following years, companies specializing in cyber security solutions began to develop patch management tools that also offered the ability to automate the patch process.
Benefits of automating patch management
In most patch management solutions available today, automated patch deployment is a key component. With the widespread use of this functionality worldwide, let’s take a brief look at how organizations are using it:
- Lowering the patch cadence
The patch cadence refers to the time it takes an organization to test and deploy patches to required systems. According to statistics, it takes an average of 60 days to patch critical vulnerabilities, but this can be further reduced with automated patching.
The presence of an automated patch testing process ensures that the patches can be safely installed on the systems. As a next step, the automated deployment workflow will seamlessly deploy the patches to the required machines.
This fully automated workflow eliminates wasted time, which is crucial when fighting critical vulnerabilities and zero-day exploits.
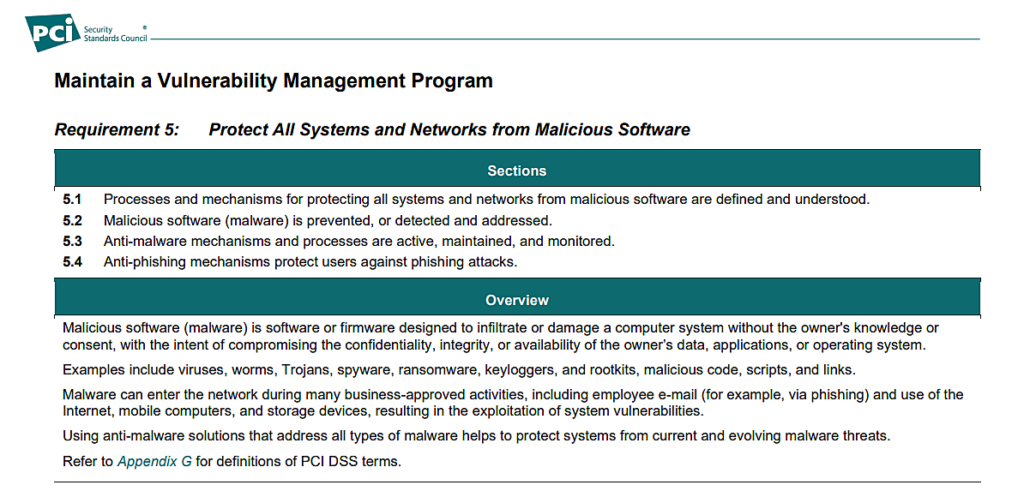
- PCI DSS 4.0 compliance
Regulatory guidelines such as the PCI DSS require companies to achieve a certain level of compliance. Requirement 5 of PCI DSS 4.0 explains how companies should maintain a vulnerability management program.
While most of these requirements can be met by a solution that specializes in unified endpoint management and security, automation in patching acts as the icing on the cake if you specifically use a patch management solution.
This recursive functionality automatically scans the network to detect malware and implements the required patches.
- Reduce human error
In an enterprise with a large number of systems, the number of patches released each month certainly runs into the hundreds. From different operating systems to third-party applications, each system has different requirements and therefore different sets of applications installed on it.
Now imagine what would happen if a critical patch had to be applied to fix a zero-day or high severity vulnerability. Testing the patches and then manually applying them to all the systems themselves would be a Herculean task.
And what if one or a few systems are overlooked? Obviously, this would be a surefire way to compromise network security. Therefore, another advantage of automated patching is that it can reduce human error.
- Enhanced security
While it is a universal truth that critical and high severity vulnerabilities should be patched as soon as possible, lower severity vulnerabilities can also pose a serious long-term threat to a network’s security.
An automated workflow ensures that these vulnerabilities are patched according to regular cycles. In addition, automated patching ensures that the software is up-to-date when the latest updates are released.
But is automated patching only about these benefits?
While it is undeniable that automating the patch management process will give enterprises the edge they need to detect vulnerabilities, there are also some prevailing doubts about its effectiveness.
- End-user disruption: Is this still a thing?
One of the biggest objections to automated patching is disruption to end users. If patches are rolled out automatically, the question is whether enterprise users can keep their work before the system or application is updated.
While this would have been a real concern a few years ago, that is no longer the case. Today, patch management solutions offer administrators advanced functionalities that allow them to customize a patch deployment to meet the needs of their enterprise.
This means that administrators can choose to give end users the option to skip or postpone patch deployment (if they are held up with important tasks). In addition, administrators also have the option to deploy these patches on the unpatched systems after a certain number of days from the date they skipped the patch.
- (Unplanned) downtime
For mission-critical machines, it is difficult to plan for downtime, and we can all agree on that. Another common concern is that automated patch implementation can cause unforeseen downtime in certain systems.
But can this be prevented? The answer is yes!
For such critical systems where downtime is difficult to plan in advance, administrators can implement required patches directly using a Self Service Portal. This allows administrators to install required patches based on their own schedule, i.e., when downtime can be scheduled without causing a ripple effect on business productivity or user experience.
- What if the patches affect system performance?
Often patches, once installed in the systems, can lead to irregularities in the systems, affecting productivity. While a workflow for testing patches can mitigate this to a greater extent, removing or rolling back these problematic patches can also fix the problems immediately.
The verdict?
While automation of the patch management workflow undoubtedly has benefits, there are also many concerns about its effectiveness. However, as we saw above, most modern patch management solutions such as Patch Manager Plus have mitigation mechanisms to negate any potential drawbacks.
Therefore, it is safe to conclude that automation of patch management is worth the hype, provided that the patch solution has functionalities to ensure that end-user productivity is always out of harm’s way.